File Types In Graphic Design: Complete Breakdown
- Anas Khan

- Jan 9, 2022
- 6 min read

Have you ever had a wave of confusion over when a designer asks, “Can you please supply your company logo as a vector file?” Or maybe they need a .PNG file for your website’s header image.
What is a vector file? And why does Papua New Guinea have a file-type?
As a graphic designer, it is extremely important to use the correct file-types for specific applications. Having the incorrect file-type could potentially lessen the desired look you were hoping for. To help prevent confusion we have put together a go-to list of design file-types that will fill you with confidence and help you understand the difference between a vector and Papua New Guinea file, I mean .PNG file. File types are also known as file extension.
Table Of Contents
Also Read: 7 Process To Master Logo Designing In 2022
Understanding the distinctions among different file types will help you correctly save, send, and manage every digital project you work on. Unless you’re a designer, you’ve probably never worked with a .PSD or an .INDD file, but that doesn’t mean you never will. This guide will help clear up the misunderstandings you might have about file types and maybe introduce you to a brand new one along the way.
RASTER FILE VS VECTOR FILE
Before diving into the different file types you might encounter, it’s important to know the distinction between a vector and a raster. Raster images are made up of pixels, or blocks of colors, to form an image. The pixels have a defined size depending on the resolution of your image.

If you try to make an image with a very low resolution into a very high resolution, the pixels will stretch and become distorted. It is impossible to resize raster images without compromising their resolution as they are already compressed. To prevent this, save your raster files at the exact same dimensions needed for your project. JPEGs, GIFs, and PNGs are all raster-supporting file types. Vector images resolve this issue.
Also Read: Why Branding Is So Important In 2022?
Also Read: 10 Common Mistakes Designers Make #1
They are far more flexible and are constructed with proportional formulas instead of pixels. Your logo was most likely created in a vector program, like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDraw. A vector image can be stretched or shrunk as much as you like—without looking pixelated and without compromising the resolution. EPS, AI, and PDF are all vector-supporting file types.
RASTER FILES
Raster Image files are compressed, these files are ‘Pixel based’ meaning the resolution and the quality of the file is limited. Using a JPEG or PNG logo image will not be able to be scaled to huge billboards or posters. This is because they are built up in pixels, meaning once you begin to stretch these images to larger scales the pixels are stretched themselves. This results in a pixelated image.
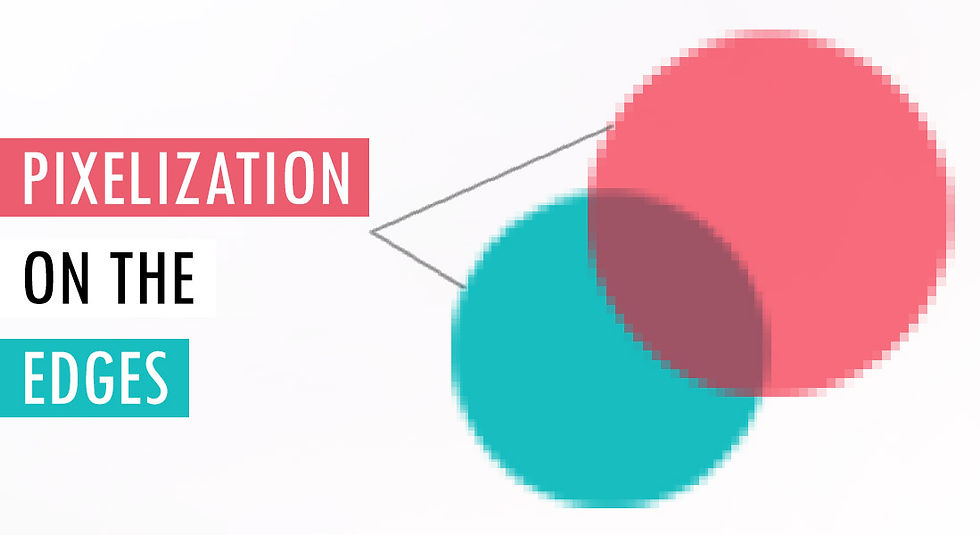
1. Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPG)
Used For:
File choice for banner ad publishers
Medium and low resolution web-use
Proofing and sharing work-in-progress design work with clients
Handy To Know:
Quick load time for web
Photos are compressed and smaller in size
Constraints:
Does not support background transparency
Does not retain its quality when rescaled
Flat image that is non-editable
2. Portable Network Graphics (PNG)
Used For:
Transferring images on the internet
High quality web images
Handy To Know:
Files can be created with transparent backgrounds (great for company logos and icons)
Compressed file sizes allow for quick load times
Displays crisp and clean on digital applications
Constraints:
Not ideal for printing
Cannot be scaled over its pixel width
Flat image that is not easily editable
3. Graphics Interchange Format (GIF)
Used For:
Web animations
Social Media Memes
Short inaudible clips
Handy To Know:
Files can be created with transparent backgrounds
Perfect for emails and web graphics
File size is small
Constraints:
GIF files are low resolution
Support only 256 colors
4. Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
Used For:
Commonly used in the photography sector
If you’re printing large photos – use this format
Storing large documents
Handy To know:
Largest raster file type
Reliable and never lose quality
Use them for saving photographs for print
Scans high quality documents
Constraints:
Never use this file type for saving web graphics
Take more time to load
Takes more space
5. RAW - Unprocessed data from digital camera
Used For:
Used by photographers and design professionals.
Store all the unprocessed and processed data from an image captured with a digital camera
RAW file allows the image to be in the absolute most highest quality
Handy To Know:
They are high quality and have high resolution
They are very large
Best used when shooting and editing photos
Make sure to save as a JPEG or TIFF when exporting
Constraints:
Most print companies won’t accept RAW files to send to print.
6. Bitmap Image File (BMP)
Used For:
Contains uncompressed data and displaying high-quality digital images
Store bitmap digital images and independently of the display device
Best for creating 3D UV texture maps
Handy To Know:
Creates lossless image quality
Allows open and re-save the image without degrading the integrity
Constraints:
Does not support background transparency
Not recommended for photographs, static graphics and animated graphics
Lack of compression generally creates larger file sizes
7. Photoshop Document (PSD)
Used For:
Primarily used to create and edit raster images not vectors
PSD Files are purely the original editable photoshop files
PSD files can be created and opened only with Adobe Photoshop
Handy To Know:
This file type allows for transparency and multiple layers
Photoshop is able to export a PSD file into a wide range of file types, including JPGs, PNGs, and PDFs
Can resize any image to fit whichever project you’re working on.
Vector layers can be contained in a Photoshop file
All Photoshop files can be exported in all the above raster formats.
You should use PSD files when retouching photos, editing digital artwork, creating web images and creating frame animations or videos.
Constraints:
Photoshop is a prerequisite
Large storage capacity due to layers
VECTOR FILES
All the logos we create are vectors, this is because they are made up of points, lines and curves that are based on mathematical equations rather than pixels like raster images. This means that no matter how large or small you make the vector or how close you zoom in all them lines, curves and points stay pristine and smooth. Logos need to be in a vector format purely so it can be scaled to large shop signs, window graphics, billboards or scaled smaller to a T-Shirt embroidery or for any print work.

Also Read: 10 Tips To Finish Your Project On Time
Also Read: 10 Best Plugins To Use In Photoshop #1
1. Adobe Illustrator File (AI)
Used For:
Logo and illustration design
Creating multi-layered/multi-paged artwork
Prototyping websites
Handy To Know:
Scalable to any size without losing image quality
Supports transparency
Full editing capabilities within Adobe Illustrator
Vector-based working file for digital artists and web developers
Constraints:
Can only be edited in Adobe Illustrator
2. Encapsulated Postscript (EPS)
Used For:
Logos and illustrations
Infographics
Icon design
Handy To Know:
One of the most preferred formats by digital designers and other third-party creatives
Single page vector-based drawing that can be scaled to any size
Supports transparent backgrounds
Fully editable artwork
Retains image quality
Can be exported to various file types
Constraints:
Can only be edited using design software such as Adobe Illustrator
3. Portable Document Format (PDF)
Used For:
Digital versions of hard copy documents or publications
Sharing previews of work without losing image quality
Universally viewable by computers
Emailing documents
Both print and digital
Digital downloads
Handy To Know:
Can be opened and edited in Adobe Illustrator
Illustrator and Photoshop files can be saved as PDF
PDFs can contain both raster and vector images
Constraints:
Not always suitable for viewing on smaller mobile devices
Can only be edited using design software
4. Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
Used For:
It is a standard graphics file type used for rendering two-dimensional images on the internet.
SVG has become an essential web design format
Even better than JPEG, PNG, and GIF
Handy To Know:
SVG can be scaled to any dimension without losing quality
SVG files are also easily editable just like changing a word in a text document
SVG can be altered using JavaScript or CSS
SVG can be bring back into Illustrator to edit
SVGs are scalable they can be saved at a minimal file size.
Constraints:
Cannot support as much detail
SVG doesn't work on legacy browsers
5. Corel Draw File (CDR)
Used For:
Logo, banners and UX designs
Creating multi-layered/multi-paged artwork
Vector graphic images and drawings
Handy To Know:
Scalable to any size without losing image quality
Supports transparency
Contains text, lines, shapes, images, colors and effects
Best for client and printing work
Constraints:
Does not work with Adobe apps
Can only be edited in CorelDraw and Inkscape
Now that we have covered the ins and outs of common design file types, their uses and the differences between them, you can supply and share with confidence!





























getintopc par productivity aur office users ke liye helpful apps uploaded hoti hain.https://getintopc.tr/
q
Free downloads simplified every day by getintopc.https://getintopc.tr/
Get unlimited free apps daily through getintopc.https://getintopc.tr/
Professionals depend daily on getintopc. https://getintopc.tr/